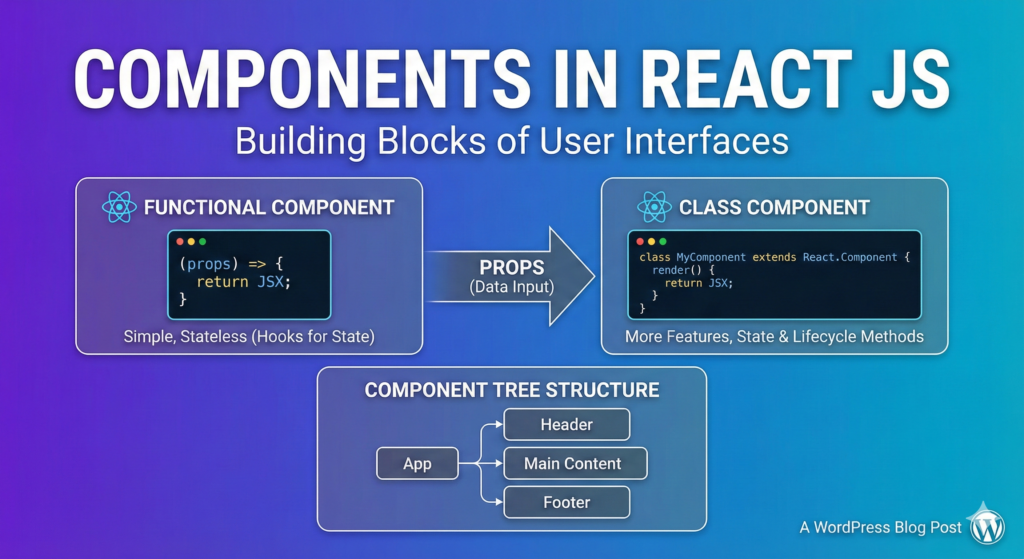
In React, a component is a piece of code that represents a part of a user interface. Components are the building blocks of a React application, and can be reused throughout the application.
There are two types of components in React: functional components and class-based components.
Functional components are simple functions that accept props (short for properties) as an argument and return a React element. They are often used for components that are presentational only, and do not have their own state. Here is an example of a functional component in React:
import React from 'react';
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}Class-based components are JavaScript classes that extend the React.Component base class. They have their own state and lifecycle methods, and are often used for components that need to manage state or perform side effects. Here is an example of a class-based component in React:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Welcome extends Component {
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>;
}
}In both cases, the component is a function or class that returns a React element, which is a description of a part of the user interface. The element can be a DOM element, or it can be a custom component defined by the developer.
Components can also have their own internal state, which is an object that stores information about the component. The state can be changed, and the component will re-render itself to reflect the new state. In class-based components, the state is stored in the state property, and can be accessed using this.state. In functional components, the state is managed using the useState hook.
Overall, components are a crucial concept in React, and understanding how to use them is essential for building applications with React.