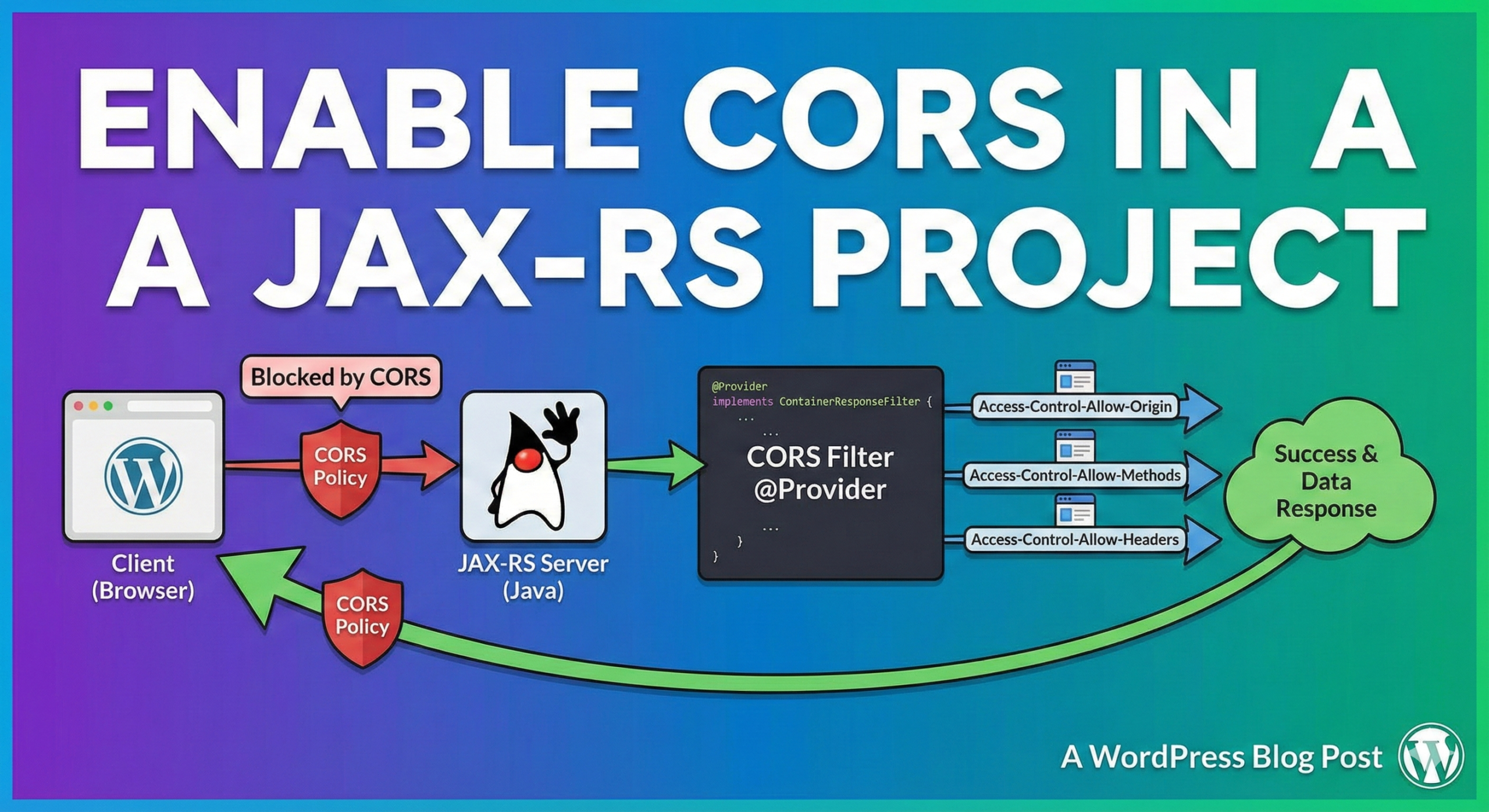
Enable CORS in a JAX-RS Project
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a security feature that restricts web pages from making requests to a different domain than the one that served the web page. If you are developing a JAX-RS project and want to enable CORS, there are a few different approaches you can take.
One approach is to use a JAX-RS filter to add the necessary CORS headers to the response. Here is an example of how you might do this:
@Provider
public class CORSFilter implements ContainerResponseFilter {
@Override
public void filter(ContainerRequestContext requestContext, ContainerResponseContext responseContext) throws IOException {
responseContext.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
responseContext.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "origin, content-type, accept, authorization");
responseContext.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
responseContext.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS, HEAD");
responseContext.getHeaders().add("Access-Control-Max-Age", "1209600");
}
}To use this filter, you will need to register it with your JAX-RS application. Here is an example of how you might do this:
public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public Set<Object> getSingletons() {
Set<Object> singletons = new HashSet<>();
singletons.add(new CORSFilter());
return singletons;
}
}Another approach is to use a third-party library like the CORS Filter library. To use this library, you will need to add it as a dependency in your project and register the CORS filter with your JAX-RS application. Here is an example of how you might do this:
public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public Set<Object> getSingletons() {
Set<Object> singletons = new HashSet<>();
singletons.add(new CorsFilter());
return singletons;
}
}There are also other approaches you can take to enable CORS in a JAX-RS project, such as using a servlet filter or configuring the CORS headers directly in your web server or application server.